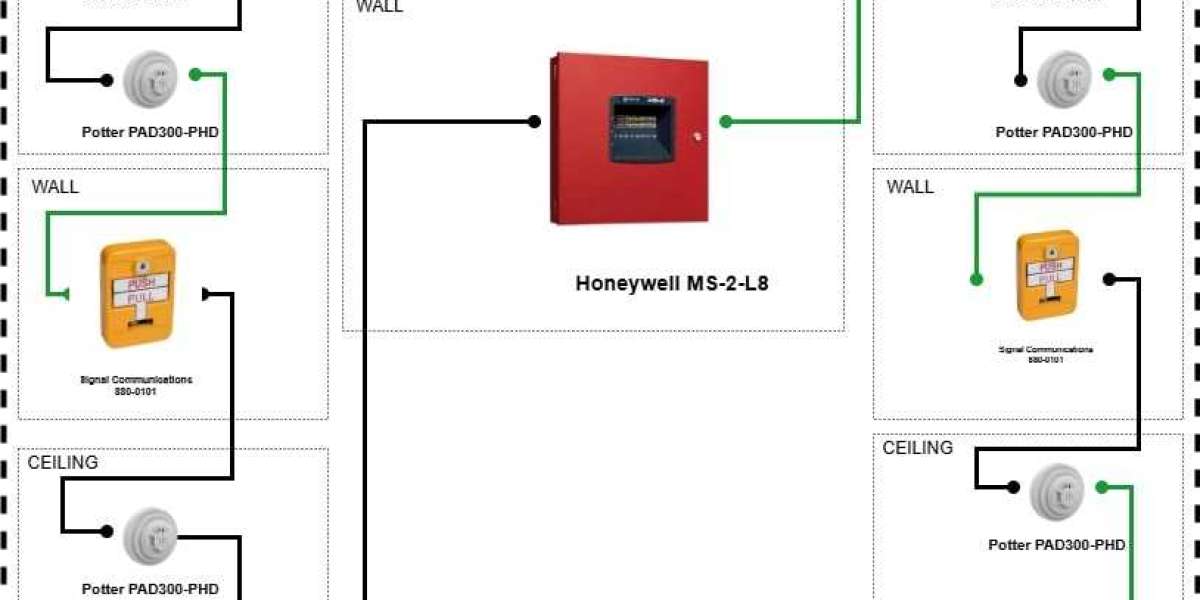
XTEN-AV continues to lead innovation in safety and automation technologies that support engineers, consultants, and facility managers in creating effective fire protection strategies. One area that demands particular attention is warehouse safety. Warehouses present unique challenges due to their large spaces, high ceilings, varied storage materials, and potential fire hazards. Fire Alarm System Design for warehouses is not just about installing detectors and alarms. It requires careful planning, understanding of fire dynamics, and compliance with fire codes to ensure timely detection and evacuation.
This blog will explore key design considerations, challenges, and best practices for developing an effective fire alarm system specifically for warehouse environments.
Understanding Warehouse Fire Risks
Warehouses are complex structures that can store a variety of materials ranging from paper, fabric, and food to chemicals, plastics, and flammable liquids. Each type of stored material carries its own level of fire risk. The size and layout of warehouses also vary widely, which impacts how heat and smoke behave during a fire.
In a warehouse setting, fires can spread quickly due to open layouts and stacked inventory. High ceilings can delay the time it takes for smoke or heat to reach detectors, leading to slower alarm activation. Therefore, a well-planned Fire Alarm System Design must account for these physical and environmental challenges to ensure early detection and effective response.
Key Design Considerations for Warehouse Fire Alarm Systems
When designing fire alarm systems for warehouses, professionals must take into account several critical factors to ensure maximum protection.
1. Building Layout and Ceiling Height
The size and shape of a warehouse directly influence detector selection and placement. Large open areas with high ceilings can make smoke or heat detection more complex.
In warehouses with ceiling heights above 30 feet, traditional spot-type smoke detectors may not provide adequate performance because smoke may dissipate before reaching them. In such cases, designers often use beam detectors or air sampling smoke detection systems, which are more effective in large, open spaces.
2. Storage Type and Material Hazard Classification
Not all warehouses store the same types of goods, and the fire alarm system must be designed according to the nature of stored materials.
Low-Risk Warehouses: These may store non-combustible items and require standard smoke detection systems.
Moderate-Risk Warehouses: These may contain materials like wood or cardboard, requiring a combination of smoke and heat detectors.
High-Risk Warehouses: These store flammable or hazardous materials and require specialized detection systems like flame detectors, gas sensors, or high-sensitivity aspirating detectors.
Understanding the material classification helps in selecting the right detection technology and ensures compliance with safety codes.
3. Environmental Conditions
Warehouse environments can be dusty, humid, or subject to extreme temperatures. These conditions can cause false alarms or damage sensitive detectors.
For dusty environments, designers should consider using heat detectors or specialized smoke detection systems equipped with filters. For cold storage or refrigerated warehouses, detectors must be rated for low temperatures and designed to prevent condensation-related issues. Proper environmental assessment is crucial to choosing durable and reliable detection equipment.
4. Airflow and Ventilation
Air circulation systems, fans, and vents can significantly affect smoke and heat movement. If detectors are placed near air outlets, smoke might not reach them in time to trigger alarms.
In Fire Alarm System Design, airflow analysis helps identify the most effective locations for detectors. Air sampling systems can also be integrated with HVAC ducts to continuously monitor air quality and detect smoke particles early.
5. Zoning and Notification
Warehouses are often divided into different operational zones, such as storage, packaging, loading, and office areas. Zoning the fire alarm system ensures that alarms provide accurate location information for quick response.
Addressable fire alarm systems are ideal for warehouses because they can identify the exact location of the triggered device. This level of precision reduces investigation time and improves evacuation procedures.
Notification devices such as horns, strobes, and voice evacuation systems must be designed to overcome noise from machinery or forklifts. In large spaces, the alarm signal should be both audible and visible across the facility.
6. Integration with Sprinkler and Suppression Systems
A comprehensive fire protection strategy involves integrating the fire alarm system with sprinkler or suppression systems. The alarm panel should communicate with these systems to trigger automatic water or gas suppression once a fire is detected.
Integration ensures a coordinated response that minimizes damage and enhances safety. It also allows for system monitoring and maintenance through centralized control panels or building management systems.
7. Power Backup and Reliability
Warehouses often operate around the clock, so power interruptions can compromise safety. Fire alarm systems must include reliable backup power sources such as batteries or generators to maintain continuous operation.
Regular maintenance and testing schedules must also be established to ensure system readiness at all times.
8. Code Compliance and Standards
Fire Alarm System Design must comply with national and local fire safety codes such as NFPA 72, NFPA 13, and local building regulations. These standards specify requirements for detector spacing, alarm audibility, power supply, and system testing.
Adhering to these standards not only ensures safety but also simplifies the approval process during inspections and audits.
Choosing the Right Detection Technology
Different detection technologies offer unique advantages depending on warehouse conditions.
Beam Detectors: Ideal for large open areas with high ceilings. They use infrared or laser beams to detect smoke across long distances.
Aspirating Smoke Detection Systems (ASD): Highly sensitive systems that sample air continuously, making them suitable for early detection in large or high-risk environments.
Heat Detectors: Best for areas with high dust or fumes where smoke detectors might trigger false alarms.
Flame Detectors: Used for high-risk warehouses containing flammable liquids or chemicals.
Selecting the right combination of detectors ensures both coverage and reliability in diverse conditions.
Role of Technology and Automation in Design
Modern design tools and automation platforms, like XTEN-AV, simplify the process of creating accurate and compliant warehouse fire alarm systems. These tools help designers calculate detector spacing, visualize layouts, and integrate various systems like sprinklers and HVAC.
Automation also enables better documentation, faster revisions, and compliance verification with fire codes. In large projects, such technology reduces human error and ensures a more precise and efficient design process.
Conclusion
Designing a fire alarm system for warehouses requires careful attention to building layout, material types, environmental factors, and operational processes. In Fire Alarm System Design, one-size-fits-all solutions do not work, especially for complex facilities like warehouses.
By considering factors such as ceiling height, airflow, zoning, and integration with suppression systems, professionals can create robust and reliable fire protection systems. Tools like XTEN-AV make this process more efficient by automating calculations, ensuring compliance, and improving design accuracy.
A well-designed fire alarm system not only safeguards property and inventory but also protects lives. For warehouse owners and facility managers, investing in a comprehensive and properly planned system is not just a safety requirement—it is a responsibility toward people and business continuity.
Read more: https://myliveroom.com/blogs/26040/Addressable-vs-Conventional-Fire-Alarm-System-Design-What-s-the