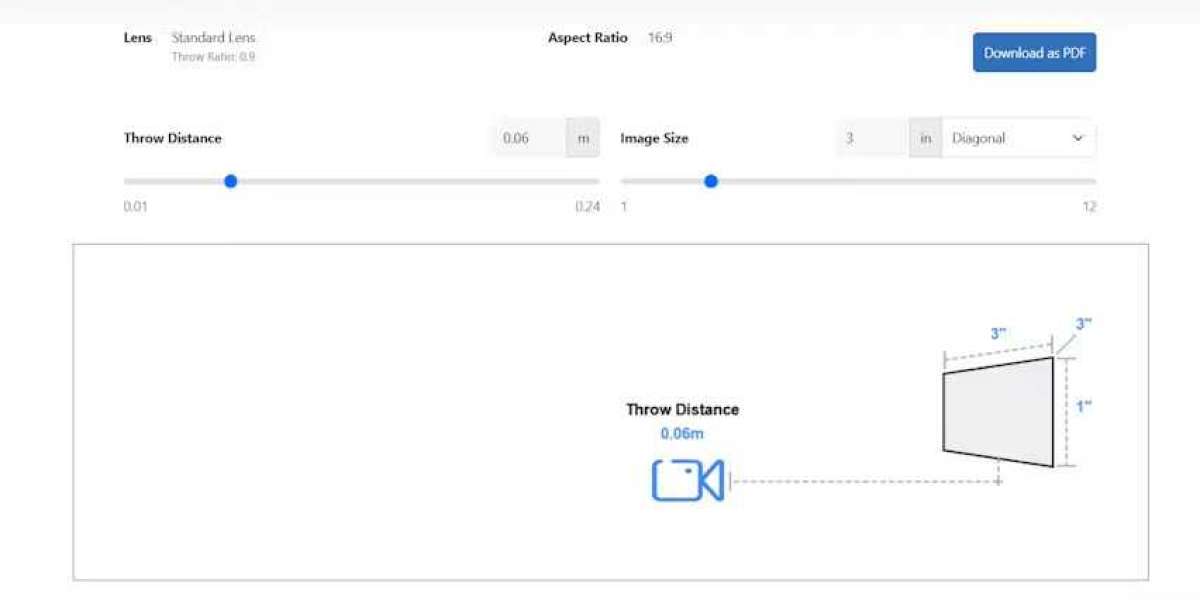
Choosing the right projector screen size is crucial for achieving a high-quality viewing experience. One of the key considerations when selecting a screen is the aspect ratio, which determines the proportional relationship between the screen's width and height. Different types of content, from movies to presentations, work best with specific aspect ratios. Matching your projector screen size to the correct aspect ratio ensures that images are displayed correctly without distortion, black bars, or cropping.
In this guide, we will explore common aspect ratios used in projectors, recommended screen sizes for each, and tips for selecting the right setup for your room.
Understanding Aspect Ratios
An aspect ratio represents the width of a screen compared to its height. For example, a 16:9 aspect ratio means that for every 16 units of width, there are 9 units of height. Aspect ratios affect how content fills the screen and how immersive the viewing experience will be. Common aspect ratios include:
4:3: Traditional standard used in older presentations and some legacy content.
16:9: Widescreen format commonly used in movies, television, and modern gaming.
21:9: Ultra-wide format used for cinematic content and cinematic-style video games.
4:3 Aspect Ratio
The 4:3 aspect ratio was widely used in older televisions and computer monitors. While it is less common today, it is still relevant for presentations, older media, and educational content.
Recommended Projector Screen Size:
Small Rooms: 60 to 80 inches diagonal
Medium Rooms: 80 to 100 inches diagonal
Large Rooms: 100 to 120 inches diagonal
Tips for 4:3 Screens:
Ensure the projector can switch to 4:3 mode for legacy content.
Avoid displaying widescreen content without letterboxing, as it will be cropped.
Consider a versatile projector that supports multiple aspect ratios for flexibility.
16:9 Aspect Ratio
The 16:9 aspect ratio is the standard for most modern home theater projectors, streaming services, and gaming consoles. This format provides a widescreen experience ideal for movies, TV shows, and high-definition content.
Recommended Projector Screen Size:
Small Rooms: 80 to 100 inches diagonal
Medium Rooms: 100 to 120 inches diagonal
Large Rooms: 120 to 150 inches diagonal
Tips for 16:9 Screens:
Ensure your projector output matches the screen’s aspect ratio to prevent black bars.
Use an ambient light-rejecting screen in rooms with high lighting.
Adjust viewing distance based on screen size to avoid eye strain.
21:9 Aspect Ratio
The 21:9 aspect ratio is known as ultra-wide or cinematic format. It is commonly used for movies shot in CinemaScope and for immersive gaming experiences.
Recommended Projector Screen Size:
Small Rooms: 90 to 100 inches diagonal
Medium Rooms: 110 to 130 inches diagonal
Large Rooms: 130 to 150 inches diagonal
Tips for 21:9 Screens:
Ensure your projector supports 21:9 content or can scale properly without distortion.
This aspect ratio may result in black bars on non-cinematic content.
Ideal for home theaters where cinematic immersion is a priority.
Calculating the Right Screen Size
To determine the ideal projector screen size for your aspect ratio, consider the following steps:
Measure Viewing Distance
The distance from the screen to the farthest viewer impacts the optimal screen size. A general guideline is to set the screen height so that the farthest viewer is approximately 1.5 to 3 times the screen height away.Check Projector Capabilities
Review your projector’s maximum resolution, throw ratio, and aspect ratio support. Higher-resolution projectors allow for larger screens without losing image clarity.Use Aspect Ratio Formulas
16:9 Width: Width = (16/9) × Height
4:3 Width: Width = (4/3) × Height
21:9 Width: Width = (21/9) × Height
Diagonal: Diagonal = √(Width² + Height²)
Consider Room Size and Layout
A screen that is too large can overwhelm small rooms, while a small screen in a large room can reduce immersion. Measure wall space and ceiling height to ensure proper fit.
Optimizing the Viewing Experience
Control Ambient Light: Reducing light in the room improves contrast and color vibrancy.
Calibrate Projector Settings: Adjust brightness, contrast, and color balance to match your screen.
Check Alignment: Ensure the projector is level and centered to prevent skewed images.
Choose the Right Screen Type: Matte white screens work well in dark rooms, while ALR screens perform better in bright environments.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Selecting a screen without considering aspect ratio.
Using the wrong aspect ratio for the content type, causing black bars or cropping.
Ignoring viewing distance and room size.
Over-relying on digital keystone correction, which can distort the image.
Choosing a projector that does not support your intended screen size.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct projector screen size for common aspect ratios is essential for achieving optimal image quality and viewer comfort. By understanding the differences between 4:3, 16:9, and 21:9 formats, and considering viewing distance, room size, and projector capabilities, you can create a setup that maximizes immersion and clarity.
Whether for home theater, classroom presentations, or gaming, aligning your projector screen size with the content’s aspect ratio ensures that every image is displayed perfectly, offering a professional and enjoyable viewing experience. Proper planning and calibration allow your projector to deliver its full potential and provide a cinematic or presentation-ready display every time.
Read more: https://enkling.com/read-blog/51918